Crushing Student Protests: Bangladesh's Repression of the Quota Reform & Road Safety Movements
Two years since student protest movements mobilised in Bangladesh, there is still no accountability for human rights violations against protesters.
‘Crushing Student Protests,’ a new report launched today by civil society groups Front Line Defenders, CIVICUS and South Asians for Human Rights (SAHR), highlights the use of excessive force, arbitrary arrests and allegations of torture and ill-treatment by the Bangladesh security forces during the protests, as well as attacks by non-state actors perpetrated with impunity against the students.
Download Crushing Student Protests
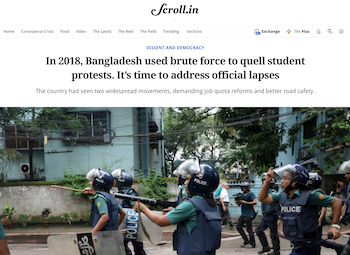
In April 2018, senior students from universities mobilised to call for reform in the quota system for government jobs. Three months later, in July and August, junior students from schools and colleges led protests demanding public transport safety reform after students were killed in traffic accidents.
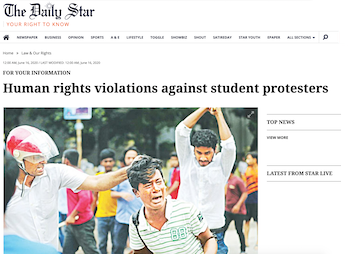
Law enforcement agencies responded to both movements with excessive force. Protesters reported that the police attacked them with teargas, rubber bullets and high pressure hot water cannons. Unidentified armed individuals believed to be members of the student wing of the ruling party, known as the Bangladesh Chhatra League (BCL), operated as an auxiliary force to Bangladeshi security forces to attack protesters with wooden logs, sticks, iron rods, and sharp weapons. They used social media to intimidate, harass and threaten protest leaders and organizers.
An activist from Jagannath University in Sadarghat, Dhaka said that on 20 April 2018, he was attacked by BCL members: “They accosted me and dragged me to a corner. There were 12 people, and they beat me up, and cut my lip…They beat me until I was senseless and left me there.”
Police also arbitrarily arrested protesters and filed multiple cases against them without specifying names, detaining students at will. Some reported torture and ill-treatment in detention.
One activist arrested on 1 July 2018 in the Bhasantek area of Dhaka related his experience of being beaten up for a full day by security forces. “They made me lie down on the floor, with my arms handcuffed, and several policemen beat me with rods,” he said. “I bled on the floor, and they made the others detained clean the floor.”
Bangladeshi journalists also were assaulted and detained as part of government efforts to control the narrative and silence critical voices.
One of those arrested was 63‑year‑old Shahidul Alam, a well-known photojournalist and activist. He was detained by plainclothes policemen on 5 August 2018, hours after giving an interview to Al Jazeera English on the student protests and charged a day later under the Information and Communication Technology (ICT) Act for making "false" and "provocative" statements. Alam told reporters that he had been beaten in police custody.
“The failure to hold anyone accountable for the violence against protesters points to deeply ingrained impunity in Bangladesh. We demand a prompt and independent investigation into all reports of violence by the police and non‑state actors against human rights defenders, journalists and protesters, and for those responsible to be brought to justice,” said Sultana Kamal, noted Bangladeshi Human Rights Defender and Chairperson of SAHR.
“The police must drop all charges against the student human rights defenders and protesters and review the convictions of protesters and other individuals prosecuted for exercising their rights to freedom of expression and peaceful assembly,” said Roshmi Goswami, SAHR bureau member from India who took part in the joint international mission.
The crackdown occurred just prior to elections held later in 2018, indicating the kind of actions the ruling party was, and remains willing, to take to hold its grip on power.
Long after the protests stopped, many student activists, their friends and family members continue to face surveillance, intimidation and harassment, effectively silencing future dissent. Social media has been deployed to intimidate and smear human rights defenders and civil society groups that supported the protests.
A prominent activist was attacked eight times after the protest movement ended. Another protest organizer has been routinely stalked by members of the National Security Intelligence (NSI).
“The authorities must end all forms of harassment, intimidation and surveillance against those involved in organising, participating or supporting the protests and ensure a safe and enabling environment for protest leaders to carry out their activism without fear of reprisals,” said Andrew Anderson, Executive Director of Front Line Defenders
The crackdown on the protests is indicative of a broader pattern of aggression and attacks by the government against critics to silence dissent. The now defunct Information Communication and Technology (ICT) Act, and its successor, the Digital Security Act, have been used to restrict freedom of expression while human rights activists, journalists and government critics have been charged or convicted for speaking up and, in some cases, forcibly disappeared.
“The Digital Security Act criminalizes many forms of freedom of expression and imposes heavy fines and prison sentences for legitimate forms of dissent. It is incompatible with international law and standards and should be amended immediately,” said David Kode, Advocacy and Campaigns Lead at CIVICUS
The human rights violations documented in this report around the protests are inconsistent with Bangladesh’s Constitution and the country’s international human rights obligations under the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights (ICCPR), UN Convention Against Torture and Other Cruel, Inhuman or Degrading Treatment or Punishment and other international laws and standards. Despite the fact that many of these issues have been raised by states, the Bangladesh authorities have failed to address them.
*************************************************
Front Line Defenders is the Ireland-based international human rights organization that works for the security and protection of human rights defenders at risk (HRDs) around the world.
CIVICUS: World Alliance for Citizen Participation is a global alliance of civil society organisations and activists headquartered in Johannesburg, South Africa and dedicated to strengthening citizen action and civil society throughout the world.
South Asians for Human Rights (SAHR) is a democratic regional network with a large membership base of people committed to addressing human rights issues at both national and regional levels. SAHR seeks to contribute to the realisation of South Asian peoples’ right to participatory democracy, good governance and justice by strengthening regional response, including regional instruments, monitoring human rights violations, reviewing laws, policies and practices that have an adverse impact on human rights and conducting campaigns and programmes on issues of major concern in the region.